Program Studi Teknologi Hasil Perikanan, Universitas Gadjah Mada, menyambut kehadiran Dr. Olivia Yofananda, S.TP., pada semester Ganjil 2023/2024. Dr. Olivia, yang akrab disapa Ibu Oliv, merupakan lulusan S1 Ilmu dan Teknologi Pangan Universitas Brawijaya dan menyelesaikan program doktor di Institut Pertanian Bogor melalui beasiswa PMDSU (Pendidikan Magister Menuju Doktor untuk Sarjana Unggul). Pengalaman akademisnya telah membentuk kecintaan Dr. Olivia pada dunia pendidikan dan penelitian, yang kemudian memotivasi beliau untuk berkarir sebagai dosen.
2024
Expo Inovasi Produk Perikanan sukses digelar pada Selasa, 19 November 2024, di bagian utara Gedung A4 Departemen Perikanan, Fakultas Pertanian, Universitas Gadjah Mada. Kegiatan ini dibuka pada pukul 11.00 WIB oleh Prof. Dr. Amir Husni, S.Pi., M.P., selaku Ketua Program Studi Teknologi Hasil Perikanan. Acara yang diikuti oleh mahasiswa Program Studi Teknologi Hasil Perikanan Angkatan 2022 ini berlangsung hingga pukul 14.00 WIB, sebagai bagian dari rangkaian Praktikum Penanganan dan Pengujian Mutu Hasil Perikanan.
Enam orang dosen Program Studi Teknologi Hasil Perikanan, Departemen Perikanan, Fakultas Pertanian, Universitas Gadjah Mada, mengikuti 2nd Southeast Asia Public Health Nutrition Conference (2nd SEA-PHN) yang diselenggarakan oleh Nutrition Association of Thailand (NAT), sebagai upaya mengikuti perkembangan ilmu pengetahuan sekaligus mendeseminasikan hasil penelitian. Seminar internasional ini merupakan pertemuan resmi dari asosiasi Southeast Asia Public Health Nutrition (SEA-PHN) yang berlangsung pada 11-13 November 2024 di Hotel Arnoma, Bangkok, Thailand, dengan narasumber dan peserta yang berasal dari lebih dari 10 negara termasuk Indonesia. Keenam dosen yang berpartisipasi dalam seminar ini adalah Prof. Amir Husni, Dr. Nurfitri Ekantari, Dr. Siti Ari Budhiyanti, Dr. Prihati Sih Nugraheni, Indun Dewi Puspita Ph.D dan Mgs. Muhammad Prima Putra, Ph.D. 2nd Southeast Asia Public Health Nutrition Conference mengusung beberapa topik: Emphasizing the nutrition issues in mother, infant, and young child (MIYC); Achieving nutrition, health and well-being for the elderly in SEA; Tackling NCDs with the implementation of real goals; Updating global trends and scientific knowledge in nutrition; and Discussion in harmonization of nutrient reference intake in SEA.
Kegiatan Kunjungan Industri (KI) merupakan salah satu rangkaian acara dari Praktikum Manajemen Industri Perikanan, Program Studi Teknologi Hasil Pertanian (THP), Departemen Perikanan, Fakultas Pertanian, Universitas Gadjah Mada. Kegiatan Kunjungan Industri dilaksanakan oleh seluruh mahasiswa Program Studi Teknologi Hasil Perikanan angkatan 2022 pada 9 November 2024. Perusahaan yang dikunjungi adalah perusahaan pengolahan ikan di Semarang, yaitu PT. Bandeng Juwana Elrina dan PT. Indomina Cipta Agung.
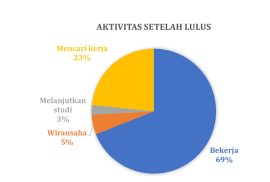
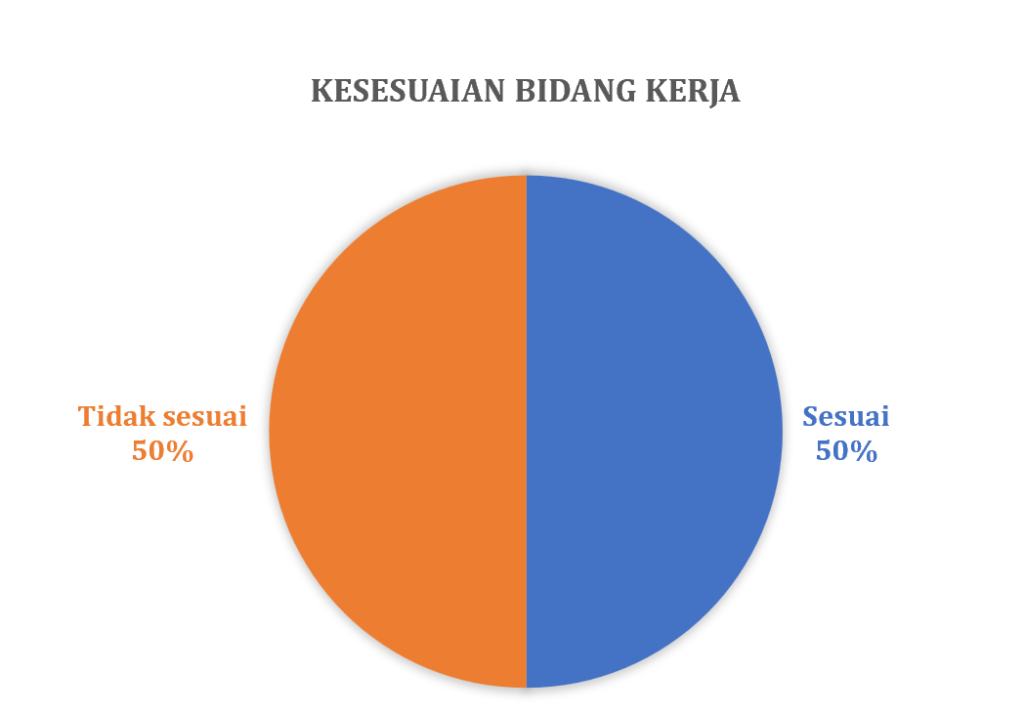
Secara rutin Prodi THP melakukan pelacakan alumni atau tracers study terhadap alumninya. Pelacakan alumni ini menggunakan sistem yang telah dibangun oleh Kantor Alumni UGM bekerja sama dengan Direktorat Teknologi Informasi melalui Simaster. Pada tahun 2023, gambaran lulusan prodi THP sebagai berikut:
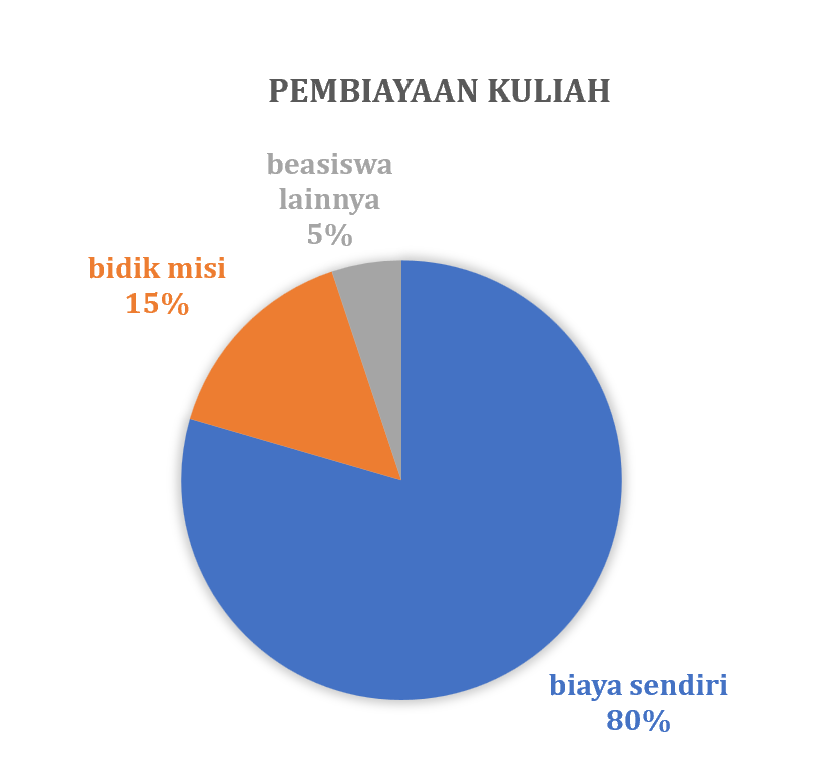
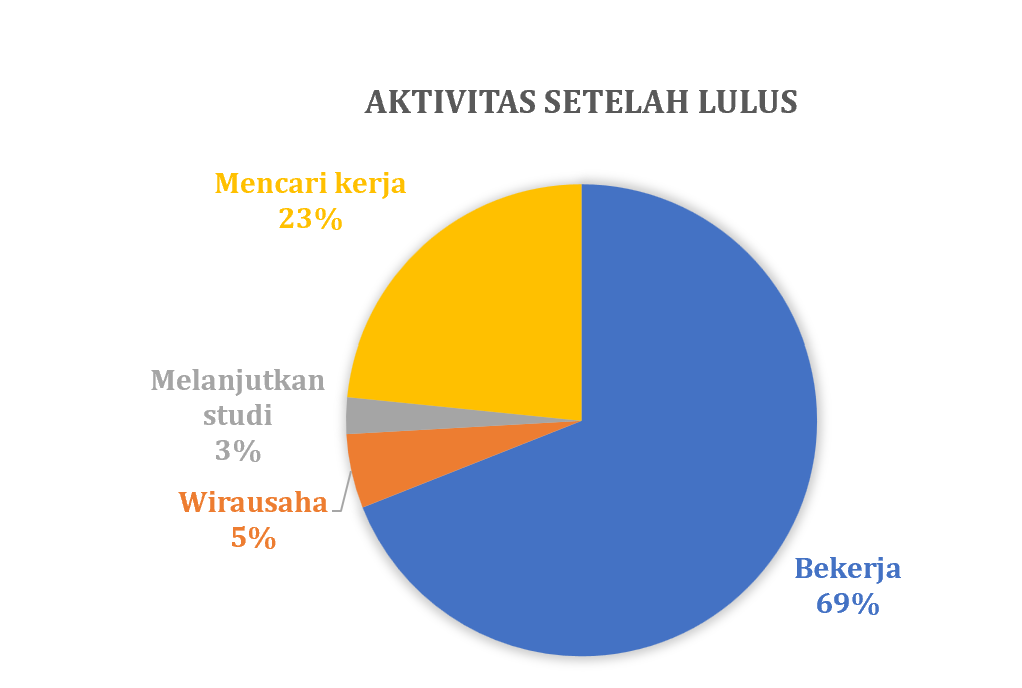
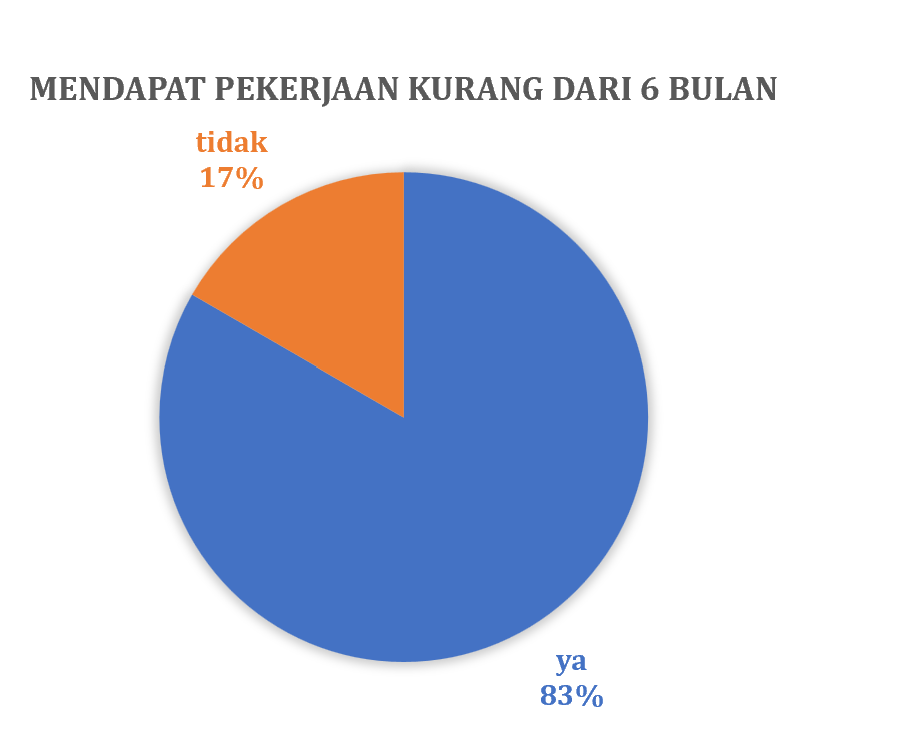
Pada hari Jumat, 26 Juli 2024, prodi Teknologi Hasil Perikanan, Departemen Perikanan Universitas Gadjah Mada menjadi tuan rumah kegiatan diskusi penyamaan kurikulum prodi THP se Indonesia. Kegiatan yang dikoordinasikan dengan Masyarakat Pengolahan Hasil Perikanan Indonesia (MPHPI) ini menjadi pertemuan lanjutan yang membahas terkait kebutuhan pembaruan kompetensi lulusan prodi THP untuk dapat memenuhi kebutuhan pasar yang terus berkembang. Pertemuan tersebut dibuka langsung oleh Dekan Fakultas Pertanian UGM, bapak Ir. Jaka Widada, Ph.D.
Masagus Muhammad Prima Putra, Muhammad Yaafi, Achmad Hanif Mardinsyah, Indun Dewi Puspita
Fish fermented products are popular products among coastal community in Indonesia. Generally, the products are naturally produced with the addition of salt without any selection of the bacterial community. This situation resulted on the variety of the final products quality. One strategy to overcome this problem is by adding a potential lactic acid (LAB), a good bacterium, in the fermentation process. We have conducted a screening of LAB from several local Indonesian fermented fish products namely Pakasam and Wadi. The first screening collected 28 isolates which characterized as LAB from Gram stain and catalase activity. The second screening was done to screen a LAB which possess antibacterial activity against common contaminant bacteria namely Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538, Salmonella sp. 230C, Escherichia coli 563 B, Citrobacter freundii CK1, Klebsiella sp. CK2, and Morganella morganii TK7. Among those 28 isolates, we selected one isolate with the highest antibacterial activity and successfully identified molecularly as Weisella sp. GMP 12. Further isolation of antibacterial substances targeted bacteriocin showed a good inhibition to Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538 with 3694 AU (Activity Unit), Salmonella sp. 230C with 2254 AU, Citrobacter freundii CK1 with 3166 AU but not to E. coli 563 B. This finding concluded that Weisella sp. GMP 12 isolated from Pakasam could be a potential candidate as a starter in the production of fermented fish products to enhance its quality.
Afrizal Syifa Kurnianto, Anjasmara Wahyu Wicaksana, Muhammad Prima Putra, Ragil Yuliatmo, Mohammad Zainal Abidin
ABSTRACT
The exploration of vegetable tanning’s natural resources is fascinating as an alternative to basic chromium sulfate for its natural abundance and considerable environmental impact. In this work, an attempt has been made to extract vegetable tannin from Caesalpinia sappan L. bark using water as a solvent with different levels of temperatures and incubation times. The highest yield efficiency was observed at 80 °C for 4 hours. The presence of tannin content and polyphenolic compounds were screened by the phytochemical analysis using Iron (III) chloride (FeCl3), sodium hydroxide (NaOH), and ensured by the thin layer chromatography (TLC), and the Fourier transform infrared (FTIR). The extracts were then determined by percentage of extract yield, phytochemical, tannin type, moisture, total solids, and tannin characteristics. The findings indicate that the extract of Secang contains 4.98±0.28% total moisture, 95.02 ± 0.28% total solids, and 72.12 ± 2.81% total soluble solids, 52.28 ± 1.79% tannins, and 19.84 ± 1.41% non-tannin. Moreover, Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) analysis revealed a clear functional group within Caesalpinia sappan L., as evidenced by the type of tannin that is condensed. The TLC assay exhibited a considerable intensity under UV lights. It included several shades of light blue and blue, which could indicate the presence of secondary metabolites and tannin. Compared to mimosa, as the commercial
standard for tanning agents in the leather industry, Caesalpinia sappan L. presents promise as an eco-friendly substitute for basic chromium sulfate and a new alternative source of vegetable tannin for the leather industry.
Mohamad Aji Ikhrami, Dini Wahyu Kartika Sari, Masagus Muhammad Prima Putra
Antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) have recently become an emerging environmental contaminants. The aquatic environment, such as a river has already become the most polluted environment and can be a driver of ARGs. The water from irrigation canal has the potential to become a hotspot of ARGs through contamination from river pollutants carried along to the irrigation canal. However, the information regarding the cross-contamination of ARGs in fish farming systems integrated with irrigation canal in Indonesia needs further study. This study investigated the occurrence of ARGs sulfonamide (sul1), tetracycline (tetA), beta lactam (blaGES), and multi drug resistance (mexF) from body water samples along the irrigation canal and aquaculture ponds which utilize irrigation water for cultivation. Sampling sites are located in the Kulon Progo Regency (Indonesia) and samples were taken during the rainy season. Gene amplification was performed using Multiplex PCR. The results showed that sul1, tetA, and blaGES were detected in 67%, 63%, and 55% of all samples. Meanwhile, mexF was only found upstream and downstream irrigation canals, which accounted for 25% of the total samples. The results of this study indicated that the Sapon Irrigation Canal has the potential to cause the spread of antibiotic resistance genes.
Amir Husni, Mohamad Gazali, Nurjanah Nurjanah, Rina Syafitri, Abdul Matin, and Zuriat Zuriat
Abstract
Lung cancer is a malignant tumor that attacks the lungs generated by carcinogenic free radicals such as cigarette smoke. Seaweed contains bioactive compounds that have the potential to reduce cancer-causing free radicals. This study aimed to determine the phytochemical content and cytotoxic activity of Halimeda tuna seaweed extract against lung cancer cells (A549). The H. tuna sample was macerated using methanol for 24 h. Cytotoxic test of H. tuna crude extract used the MTT test against A549. The crude extract was phytochemically tested and analyzed using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS). The results showed that the H. tuna crude extract had cytotoxic activity against A549 with an IC50 value of 2771 µg/mL. The phytochemical test showed that H. tuna crude extract contained flavonoids and steroids. showed the presence of fatty acid compounds including palmitic acid, oleic acid, myristic acid, palmitoleic acid and stearic acid. Based on the results can be concluded that H. tuna extract had cytotoxic activity against A549 with low cytotoxicity to be used as a chemo-preventive agent.