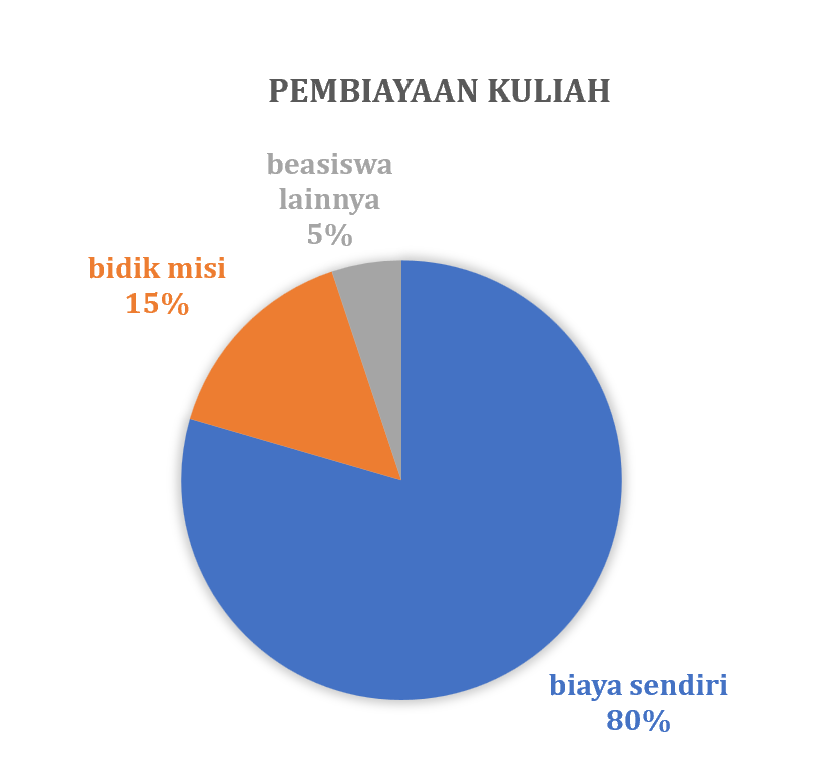
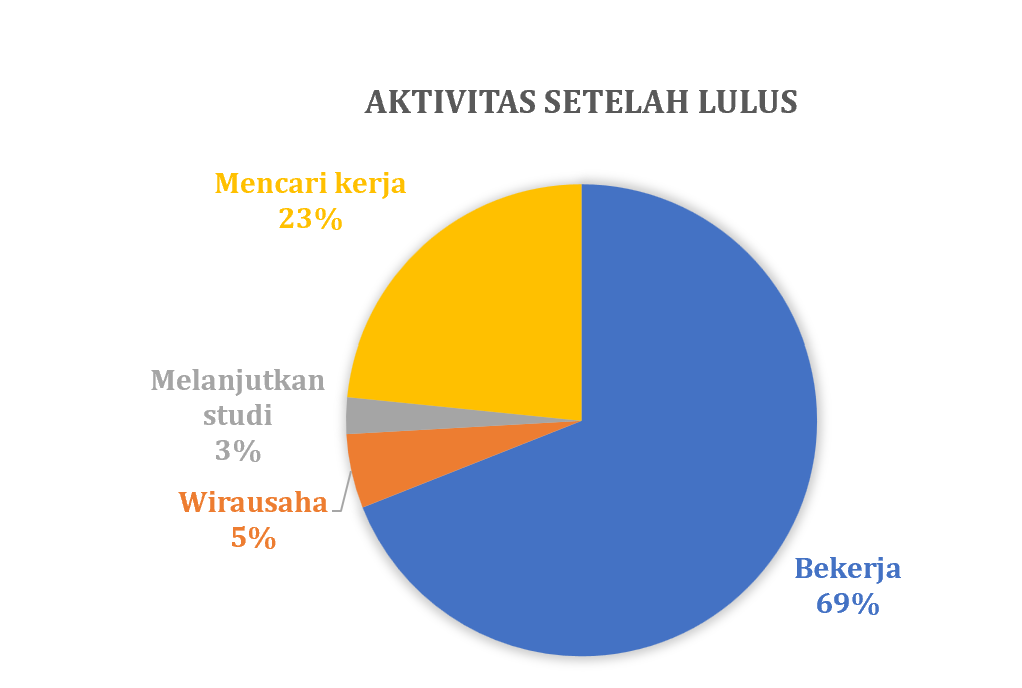
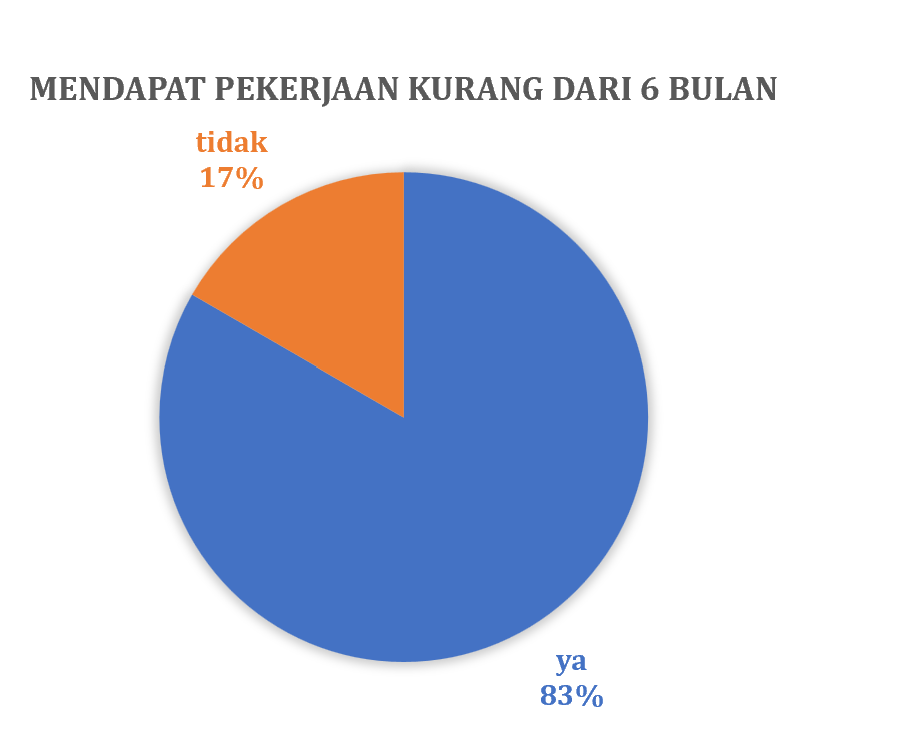
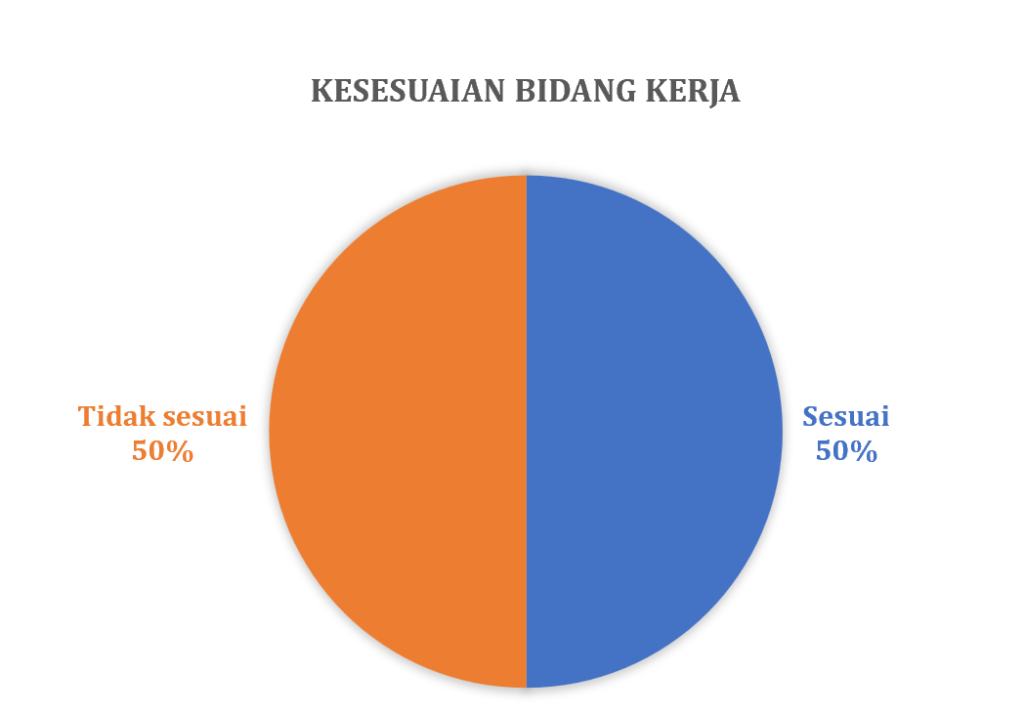
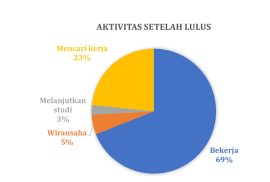
Secara rutin Prodi THP melakukan pelacakan alumni atau tracers study terhadap alumninya. Pelacakan alumni ini menggunakan sistem yang telah dibangun oleh Kantor Alumni UGM bekerja sama dengan Direktorat Teknologi Informasi melalui Simaster. Pada tahun 2023, gambaran lulusan prodi THP sebagai berikut: